ServiceComb Pack 0.4.0 Cluster : Implementation
Now you can run multiple Alpha server in High Availability (HA) mode which support to run the event scanning in the master node only. You can also turn off event table scanning for some nodes with parameter alpha.event.scanner.enabled=false . However, transaction compensation will fail when the node that enabled the event table scan is crashed.
We implemented database-based distributed lock in version 0.4.0 version, event scanning only runs on the master node in the cluster, When the master node is down, other nodes in the cluster will elect a new master node.
Quick Starts
Enable cluster support by parameter alpha.cluster.master.enabled=true.
- Start Two Alphas.
java -jar alpha-server-0.4.0-SNAPSHOT-exec.jar \
--server.port=8090 \
--alpha.server.port=8080 \
--spring.datasource.url="jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/saga?useSSL=false" \
--spring.datasource.username=saga-user \
--spring.datasource.password=saga-password \
--alpha.cluster.master.enabled=true
java -jar alpha-server-0.4.0-SNAPSHOT-exec.jar \
--server.port=8091 \
--alpha.server.port=8081 \
--spring.datasource.url="jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/saga?useSSL=false" \
--spring.datasource.username=saga-user \
--spring.datasource.password=saga-password \
--alpha.cluster.master.enabled=true
- Who Is Master
Master Node This alpha is the master
01:31:07.032 [pool-3-thread-1] INFO org.apache.servicecomb.pack.alpha.server.cluster.master.ClusterLockService - Master Node
Slave Node This alpha is the slave
01:31:31.059 [pool-3-thread-1] INFO org.apache.servicecomb.pack.alpha.server.cluster.master.ClusterLockService - Slave Node
- Switch Master Nodes
After the master node is off line, other nodes in the cluster will elect a new master node
How to make event scanning only run on the master node
Event scanning is implemented by EventScanner.java , initialize it in AlphaConfig.java , you can enable it by setting the parameter ‘alpha.event.scanner.enabled=true’, it will be instantiated EventScanner. The variable nodeStatus is the node type(Master or Slave). Later, I will introduce how nodeStatus is initialized.
@Bean
TxConsistentService txConsistentService(
@Value("${alpha.event.pollingInterval:500}") int eventPollingInterval,
@Value("${alpha.event.scanner.enabled:true}") boolean eventScannerEnabled,
ScheduledExecutorService scheduler,
TxEventRepository eventRepository,
CommandRepository commandRepository,
TxTimeoutRepository timeoutRepository,
OmegaCallback omegaCallback) {
if (eventScannerEnabled) {
new EventScanner(scheduler,
eventRepository, commandRepository, timeoutRepository,
omegaCallback, eventPollingInterval, nodeStatus).run();
LOG.info("Starting the EventScanner.");
}
TxConsistentService consistentService = new TxConsistentService(eventRepository);
return consistentService;
}
The pollEvents method of EventScanner.java for scanning events, If the master node nodeStatus.isMaster() returns true.
private void pollEvents() {
scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
() -> {
// only pull the events when working in the master mode
if(nodeStatus.isMaster()){
updateTimeoutStatus();
findTimeoutEvents();
abortTimeoutEvents();
saveUncompensatedEventsToCommands();
compensate();
updateCompensatedCommands();
deleteDuplicateSagaEndedEvents();
updateTransactionStatus();
}
},
0,
eventPollingInterval,
MILLISECONDS);
}
Construct NodeStatus in AlphaConfig.java by the following to ensure that the event scan will work regardless of whether you have configured the alpha.cluster.master.enabled parameter, Here you can see the node is a slave just after startup when cluster mode is enabled. Later, I will introduce how to switch to master.
@Bean
NodeStatus nodeStatus (){
if(masterEnabled){
return new NodeStatus(NodeStatus.TypeEnum.SLAVE);
}else{
return new NodeStatus(NodeStatus.TypeEnum.MASTER);
}
}
@Autowired
NodeStatus nodeStatus;
ClusterLockService.java is in charge of node state switching, It periodically perform lock preemption and set the node as a master after successful preemption.
@Autowired
LockProvider lockProvider;
...
...
@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?")
public void masterCheck() {
if (applicationReady) {
this.locker = lockProvider.lock(this.getMasterLock());
if (this.locker.isPresent()) {
if (!this.locked) {
this.locked = true;
nodeStatus.setTypeEnum(NodeStatus.TypeEnum.MASTER);
LOG.info("Master Node");
}
//Keep locked
} else {
if (this.locked || !lockExecuted) {
locked = false;
nodeStatus.setTypeEnum(NodeStatus.TypeEnum.SLAVE);
LOG.info("Slave Node");
}
}
lockExecuted = true;
}
}
Lock architecture
As you can see from the previous description, in the masterCheck method of ClusterLockService.java, get a lock by this.locker = lockProvider.lock(this.getMasterLock()); and determine if the lock was successful.
LockProvider.java is an interface. Currently, we provide an implementation based on JDBC. The package structure and class dependencies are as follows:
Dependencies are as follows
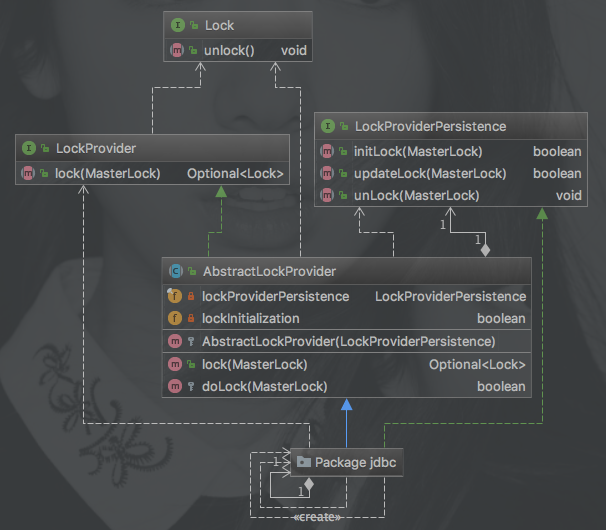
-
LockProvider.java
The interface defines the lock methods
-
LockProviderPersistence.java
The interface defines the following three persistence methods
- initLock Create a lock, try to lock and return whether the lock was successful
- updateLock Update the lock, lock it again and return it successfully (the interface design of the update lock is designed for non-long connection lock design, for example, for locking according to a fixed period)
- unLock
-
AbstractLockProvider.java
Implemented the
LockProvider.javainterface and called the internalLockProviderPersistence.javainterface for locking operations
JDBC implementation
I like to run with you, the same rhythm, the same heartbeat, I feel very good, when you fall behind, I lead everyone to run together
- JDBC class diagram
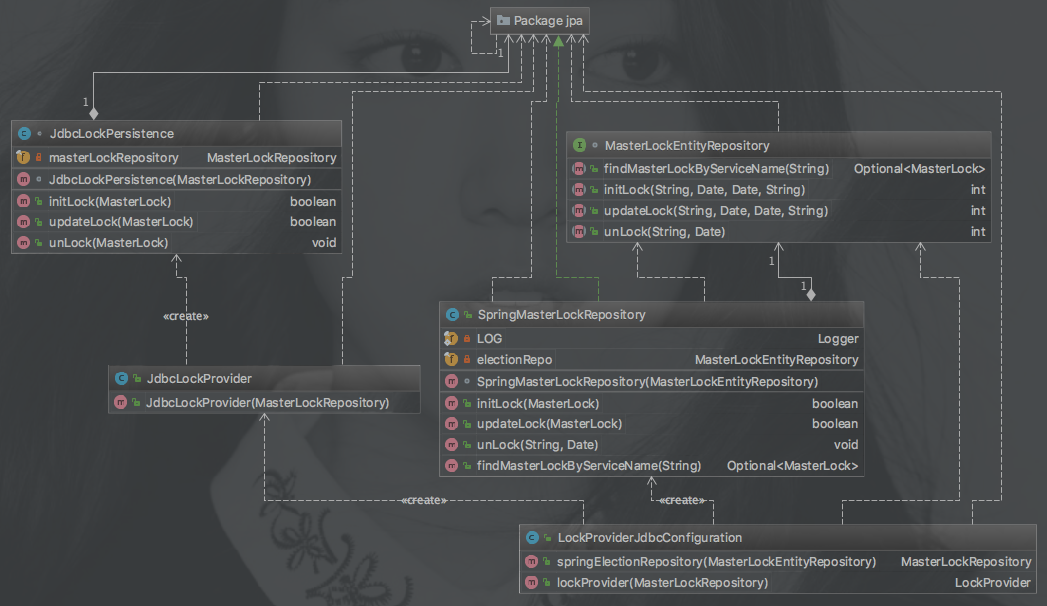
-
JdbcLockPersistence.java
Implement
LockProviderPersistence.javainterface operation database -
JdbcLockProvider.java
Inherit the abstract class
AbstractLockProvider.java, passing theLockProviderPersistence.javainterface implementation classJdbcLockPersistencein the constructor. -
LockProviderJdbcConfiguration.java
Declare a LockProvider Bean with @Configuration
-
JPA
MasterLockEntityRepository.java、SpringMasterLockRepository.java、org.apache.servicecomb.pack.alpha.server.cluster.master.provider.jdbc.jpa.*
-
Create master_lock Table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS master_lock (
serviceName varchar(36) not NULL,
expireTime datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
lockedTime datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
instanceId varchar(255) not NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (serviceName)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- serviceName Service name, this field takes the value
$ {spring.application.name} - expireTime Lock expiration time, this field takes value lockedTime + 5s
- lockedTime Last lock time
- instanceId Service instance ID, this field takes the value
$ {alpha.server.host}]:$ {alpha.server.port}
Lock processing
The process of locking/updating a lock is a cyclically repeating action, as follows:
-
ClusterLockService.javacalls the lock method ofLockProvider.javainterface once per second -
The lock method in the abstract class
AbstractLockProvider.javawill attempt to lock the iniLock method ofJdbcLockPersistence.java, and the locked SQL implementation is defined inMasterLockEntityRepository.java- If the table is empty then insert a record and return the lock successfully
- Exception caught and lock failed if there are records with the same service name field in the table
@Transactional @Modifying @Query(value = "INSERT INTO master_lock " + "(serviceName, expireTime, lockedTime, instanceId) " + "VALUES " + "(?1, ?2, ?3, ?4)", nativeQuery = true) int initLock( @Param("serviceName") String serviceName, @Param("expireTime") Date expireTime, @Param("lockedTime") Date lockedTime, @Param("instanceId") String instanceId); -
If the initLock lock fails, try to update the lock by calling the updateLock method in
MasterLockEntityRepository.java.- If the record instanceId of the same service name is the same as the instance instanceId, the update succeeds and the lock is successfully returned.
- If the record expireTime of the same service name is less than the current lock time, the update is successful and the lock is successful.
@Transactional @Modifying(clearAutomatically = true) @Query("UPDATE org.apache.servicecomb.pack.alpha.server.cluster.master.provider.jdbc.jpa.MasterLock t " + "SET t.expireTime = :expireTime" + ",t.lockedTime = :lockedTime " + ",t.instanceId = :instanceId " + "WHERE t.serviceName = :serviceName AND (t.expireTime <= :lockedTime OR t.instanceId = :instanceId)") int updateLock( @Param("serviceName") String serviceName, @Param("lockedTime") Date lockedTime, @Param("expireTime") Date expireTime, @Param("instanceId") String instanceId); -
UnLock
Reserved interface for extending other ways of locking
Other lock implementations
Other types of locks can be implemented through the LockProvider.java and LockProviderPersistence.java interfaces, such as zookeeper or redis etc.
Note
-
Need to synchronize time across multiple servers
-
Need to configure the correct time zone parameters when using MySQL database
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *